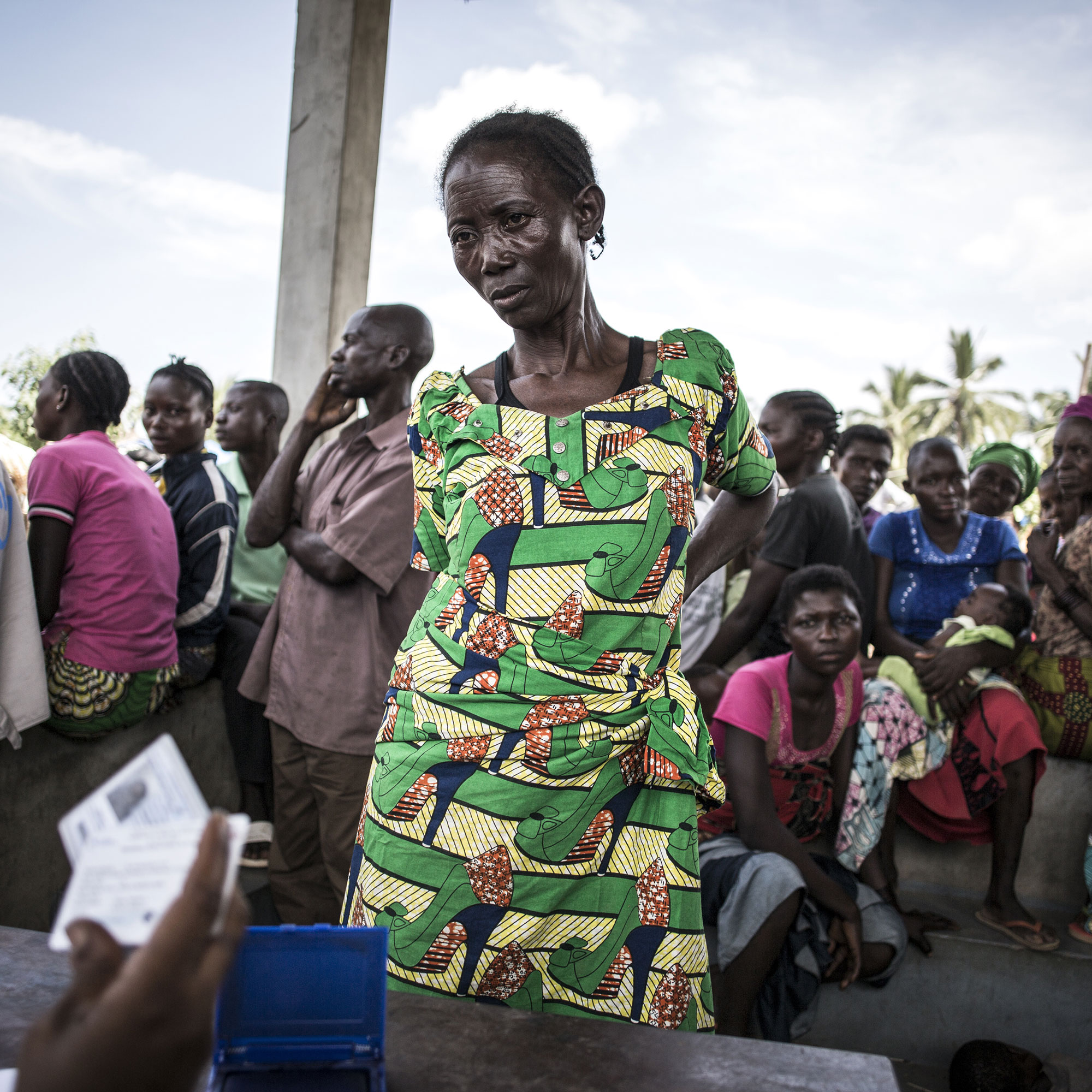
© John Wessels, HI
Background & History
Why “Leave No One Behind”?
Persons with disabilities make up about 15 per cent of the global population, recent robust data from conflict settings like Syria show a prevalence of even 29%. Many studies show that persons with disabilities face disproportional high risks of violence, abuse and death in humanitarian contexts while access to humanitarian services and protection is often considerably lower than for persons without disabilities.
Inclusive humanitarian assistance is a human right enshrined in Article 11 of the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD). To really “Leave no one behind”, humanitarian action should reach those who need it most, including persons with disabilities.
Project History
Due to these challenges the German Federal Foreign Office has been funding the “Leave no one behind!” project series for mainstreaming disabilities, since 2016. The first project phase was implemented in cooperation with the Christoffel-Blindenmission e.V. (CBM). The focus of the Phase 1 was to build up and expand the core competencies of German humanitarian actors in the field of disability inclusion. The participants started to learn about important instruments and practices, through activities such as seminars or coaching measures. After two years, the project was successfully completed and its follow-up project, Phase 2 was launched in September 2018.
The phase 2 (2018-2021) continued the capacity development and awareness raising activities of German humanitarian actors and their local partners, but included also applied research part. This was conducted by the Institute for International Law of Peace and Armed Conflict (IFHV) at the Ruhr-University Bochum. In addition, Phase 2 also significantly supported the development, translation and dissemination of the Inter-Agency Standing Committee’s (IASC) Guidelines on Inclusion of Persons with Disabilities in Humanitarian Action - the first system-wide globally accepted guidelines on inclusive humanitarian action. The IASC Guidelines are an integral part of the capacity development activities carried out by the project.
The phase 3 (2022-2024) builds onto the results, experiences and lessons of the past two phases. We will support the operationalisation of the IASC Guidelines on Inclusion of Persons with Disabilities in Humanitarian Action by further capacity building activities, tool development, local technical support and surge mechanisms as well as increased evidence base through applied research. To this end, we are working not only at the German and global level, but also directly in six pilot countries: Somalia and Somaliland, South Sudan, Uganda, Cameroon, Niger and Nigeria.

© HI
Transition from Phase 1 to Phase 3
A brief digression:
Why is it our duty to consider the needs and capacities of persons with disabilities?
On 29 March 2009, the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities became effective in Germany. It is generally referred to as UN CRPD.
The UN convention is the first legal instrument to concretise the universal human rights for persons with disabilities. The convention is fundamentally based on the inclusion of persons with disabilities and their complete and independent participation in society with equal opportunities.
Human dignity, non-discrimination and accessibility of services are of particular importance in hazardous situations and humanitarian emergencies. Therefore the contracting states shall take, in accordance with their obligations under international law, […], all necessary measures to ensure the protection and safety of persons with disabilities in situations of risk, including situations of armed conflict, humanitarian emergencies and the occurrence of natural disasters, as per Article 11 of the UN CRPD.
Hence, Germany and humanitarian assistance, funded by the German Federal Foreign Office, is obliged to take into consideration the interests, needs and capacities of persons with disabilities.